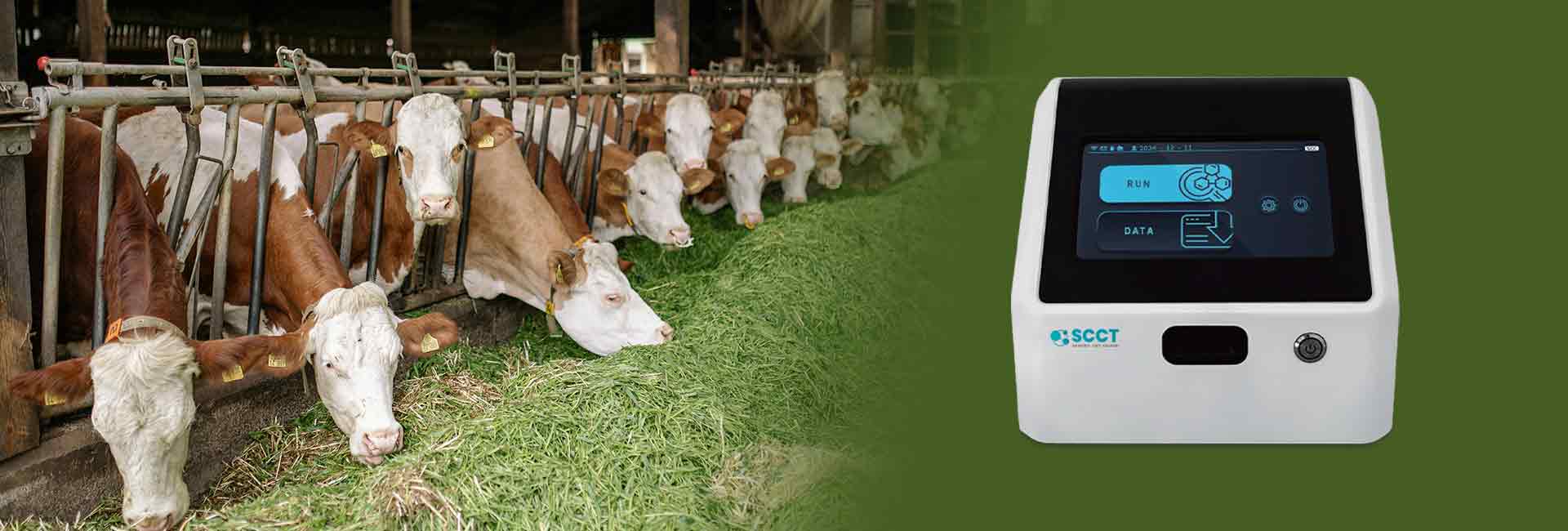

Syncing somatic cell count data with dairy herd management software supports better herd health and operational efficiency. The integration of in-line sensors enables continuous monitoring, which helps farmers detect mastitis early and maintain compliance with quality standards. Studies show that timely interventions based on this data can reduce milk production losses and improve pregnancy rates.
| Outcome | Impact of Elevated SCC |
|---|---|
| Milk Production | Lower production levels |
| Pregnancy Rates | Reduced pregnancy rates |
| Death Losses | Increased death losses |
Farmers can choose manual or automated syncing methods for greater accuracy and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Syncing somatic cell count data enhances herd health monitoring. Real-time data helps detect udder health issues early, allowing for timely interventions.
- Automated integration of data reduces human error and saves time. This method provides instant updates and supports better decision-making in dairy farming.
- Regular syncing schedules are crucial for accurate health monitoring. Farmers should sync data at least weekly to maintain reliable records and support compliance.
- Choosing the right syncing method depends on farm size and technology. Options range from manual entry to advanced automated systems, each with unique benefits.
- Data validation is essential for effective herd management. Regular checks ensure accurate records, helping farmers meet health standards and avoid financial losses.
Why Sync Somatic Cell Count Data?
Herd Health Insights
Syncing somatic cell count data with dairy herd management software provides a foundation for effective health monitoring. Farmers gain access to real-time monitoring, which allows them to track udder health and milk quality with precision. This approach supports early detection of udder health problems, such as mastitis, and enables targeted interventions. The table below highlights the main benefits of integrating somatic cell count data for herd health:
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitoring | SCC data enables precise monitoring of udder health and milk quality. |
| Identification | It helps identify inflammatory processes at individual and herd levels. |
| Targeted Interventions | Facilitates targeted interventions to manage udder health effectively. |
| Early Detection | SCC is crucial for early detection of udder health problems. |
| Surveillance | It serves as a valuable tool for recognition and prevention of infections. |
| Herd Health | Bulk milk analyses can identify herds with udder health issues. |
By using dairy herd management software, farmers can make data-driven decisions that improve overall herd health. Health monitoring becomes more proactive, reducing the risk of widespread infections and supporting milk production optimization.
Efficiency in Dairy Farming
Efficient farm management depends on timely and accurate livestock data. Syncing somatic cell count data streamlines daily operations and reduces manual labor. The following points illustrate how this process increases efficiency:
- Lowering somatic cell count is linked to increased profits for dairy farmers.
- A long-term study found that elevated SCC correlates with lower milk production, reduced pregnancy rates, and higher mortality.
- For every 100,000-cell increase in bulk tank SCC, there is a loss of 5.5 pounds of milk per cow per day.
- Faster disease detection reduces medical expenses and prevents milk loss.
- Optimized milk quality control ensures compliance with industry standards, minimizing rejected shipments and penalties.
- Automated decision-making reduces human error and saves time.
Dairy herd management software supports milk production optimization by automating health monitoring and integrating livestock data. This approach leads to cost savings, improved productivity, and consistent compliance with industry regulations.
Preparing Dairy Herd Management Software
Data Source Identification
Dairy herd management software relies on accurate and timely data collection and analysis. Farmers often gather somatic cell count data from several sources. Common sources include laboratory report, automated milking system, and somatic cell count tester. These devices provide instant udder health and milk quality information, which supports effective health monitoring and mastitis control. Advanced technologies, such as optical measurement tools and chemical reagent analyzers, also play a role in analyzing milk samples for somatic cell counts. Many farms use anonymized data from regular milk recording analysis, covering years of livestock data and milk parameters.
| Source Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Somatic Cell Count Test Kit | Provides instant udder health and milk quality information, crucial for herd management and mastitis control. |
| Advanced Technologies | Utilizes optical measurement and chemical reagents to analyze milk samples for somatic cell counts. |
Farmers should identify all relevant data sources before integrating them with their dairy herd management software.
Software Compatibility
Compatibility between data sources and dairy herd management software ensures seamless integration and data accuracy. Popular platforms, such as BoviSync, John Deere Data Sync, and FarmLogic, support a wide range of devices, including somatic cell count tester and automated milking system. Farmers should check if their chosen software can accept data from their specific devices. This step helps avoid issues during the automated transfer of data and supports advanced analytics for better decision-making. Compatibility checks also reduce the risk of data management errors and improve overall efficiency in farm management.
Tip: Review the software documentation or contact support to confirm compatibility with your somatic cell count tester and other devices.
Access and Permissions
Proper access and permissions are essential for secure data management. Farmers need to gather all necessary credentials, such as user IDs, passwords, and device authorization codes, before starting the integration process. Assigning the right permissions to team members helps maintain data accuracy and protects sensitive livestock data. Regularly updating access controls also supports compliance with industry standards and ensures only authorized users can modify or view health monitoring records.
By preparing dairy herd management software with the right data sources, compatibility checks, and access controls, farmers set the foundation for efficient and reliable data integration.
Sync Methods for Somatic Cell Count Data
Dairy farmers can choose from several methods to sync somatic cell count data with dairy herd management software. Each method offers unique advantages for accuracy, speed, and ease of use. Selecting the right approach depends on the farm’s technology, workflow, and goals for health monitoring and data-driven decisions.
Manual Entry
Manual entry remains a common method for smaller farms or those with limited technology. Farmers record somatic cell count results from laboratory reports or automated milking systems directly into dairy herd management software. This process allows for careful review of livestock data before submission. Manual entry works best for small herds or when only a few data points require updating.
Note: Manual entry can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Regular checks help maintain data accuracy.
Farmers often use manual entry to update health monitoring records, track individual cow performance, and ensure compliance with milk quality standards. This method provides flexibility but may slow down real-time monitoring and decision-making.
File Import
File import offers a faster way to transfer somatic cell count data into dairy herd management software. Many platforms support file uploads in formats such as CSV, Excel, or XML. Farmers can export livestock data from laboratory systems or automated milking systems and import it directly into their management platform.
| Supported Format | Description |
|---|---|
| CSV | Widely used for bulk data uploads |
| Excel | Allows for easy data manipulation |
| XML | Supports structured data transfer |
File import reduces manual labor and improves consistency. Farmers can batch upload health monitoring results, milk quality reports, and other livestock data. This method supports the automated transfer of data from multiple sources, streamlining daily operations and supporting advanced analytics.
Automated Integration
Automated integration represents the most efficient and accurate method for syncing somatic cell count data. Dairy herd management software can connect directly to automated milking systems, laboratory databases, and IoT devices using APIs, direct connections, or third-party tools. These integrations enable real-time monitoring and instant updates to livestock data.
The Lely MQC-C tool stands out in the dairy industry for automated integration. This system monitors somatic cell count daily, providing early detection of mastitis and supporting proactive health monitoring. Over 65% of Lely Astronaut A5 robots include the MQC-C, showing widespread adoption and trust in automated solutions.
Advanced integration tools save time and improve data accuracy in several ways:
- The Pro-Control Plus Feed Batching System streamlines feed batching, consolidating measurements and mixing, which saves labor and enhances ration accuracy.
- Integrating datasets from various sources improves dairy cattle welfare and production efficiency, which depend on multiple measurable traits.
- The use of IoT, AI, and advanced analytics in dairy herd management software automates operations, allowing farmers to focus on producing high-quality milk.
Automated integration supports data-driven decisions by providing instant access to health monitoring results and milk quality trends. Farmers benefit from reduced human error, faster disease detection, and optimized compliance reporting.
Tip: Farms that invest in automated integration tools experience greater efficiency and accuracy in livestock data management.
Choosing the right sync method depends on farm size, technology, and goals. Advanced tools offer significant advantages for large operations and those seeking real-time monitoring and automated transfer of data.
Troubleshooting & Best Practices in Dairy Farming
Common Sync Issues
Syncing somatic cell count data with dairy herd management software sometimes presents challenges. Data mismatches, sync errors, and software limitations can disrupt health monitoring and reporting. Farmers often encounter issues such as incorrect credentials, network problems, or mismatched data fields. To resolve these problems, they can follow a few practical steps:
- Check credentials, including usernames and app tokens, especially after updates.
- Use network tools like the
pingcommand to test connectivity and address timeouts. - Document field names, data types, and transformation rules to fix mismatches.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ensure real-time data access to minimize errors and enhance customer experience. |
| 2 | Use a single software solution to store all data in one place, reducing time and errors. |
| 3 | Implement a single program with multiple integrations to manage orders, deliveries, and payments efficiently. |
Tip: Verifying API keys and network connections helps prevent most sync errors.
Regular Sync Schedules
Establishing regular sync schedules supports accurate health monitoring and compliance in dairy farming. Automated or scheduled syncing ensures that livestock data remains current and reliable. Many farms choose daily or weekly syncs, depending on herd size and milk testing frequency. Consistent schedules reduce the risk of missing important updates and help maintain a clear record for audits.
Data Validation & Updates
Validating and updating somatic cell count data is essential for effective health monitoring and regulatory compliance. Farmers should:
- Monitor somatic cell count regularly to manage milk quality.
- Conduct monthly milk testing for animal-specific data.
- Identify cows with elevated SCC values quickly and react to levels above 200,000 cells/mL.
- Maintain up-to-date records to meet health and safety regulations.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) play a key role in improving milk safety and quality. Many regions set strict limits for somatic cell counts, such as 750,000 cells/mL in the United States and 400,000 cells/mL in the European Union, New Zealand, and Australia. Exceeding these limits can result in milk rejections, financial losses, and reputational damage. Keeping dairy herd management software updated ensures accurate reporting and supports compliance with industry standards.
Conclusion

Syncing somatic cell count data involves several key steps. Farmers identify data sources, check software compatibility, and select a syncing method. Many operations progress from traditional manual entry to advanced real-time integration:
- Traditional counting methods remain common.
- Rapid detection devices now support faster SCC monitoring.
- SCC standards highlight its role in milk quality and farm economics.
- Advanced syncing improves monitoring and management.
| Trend | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Real-time SCC analyzers | Early mastitis detection |
| Automated data integration | Improved herd health and profitability |
| Instant milk analysis | Enhanced production efficiency |
Starting with basic syncing and moving to automated solutions helps farms achieve better health, efficiency, and compliance.
FAQ
How Often Should Farmers Sync Somatic Cell Count Data?
Farmers should sync somatic cell count data at least once a week. Larger farms or those using automated systems may benefit from daily syncing. Regular updates help maintain accurate records and support timely health interventions.
What File Formats Do Most Dairy Herd Management Platforms Support?
Most platforms accept CSV, Excel, and XML files. These formats allow easy data transfer from laboratory systems or milking equipment. Farmers should check their software documentation for specific requirements.
Can Automated Integration Reduce Human Error?
Automated integration reduces human error by transferring data directly from devices to software. This process eliminates manual entry mistakes and ensures accurate health monitoring. Farmers gain more reliable data for decision-making.
What Should Farmers Do If Sync Errors Occur?
Farmers should first check credentials and network connections. Reviewing software documentation and contacting support can resolve most issues. Keeping software updated also helps prevent common sync errors.
Why Is Data Validation Important in Dairy Farming?
Data validation ensures that records of somatic cell count are accurate and up to date. Accurate data supports better herd health decisions and helps farms meet regulatory standards. Regular validation prevents costly mistakes.