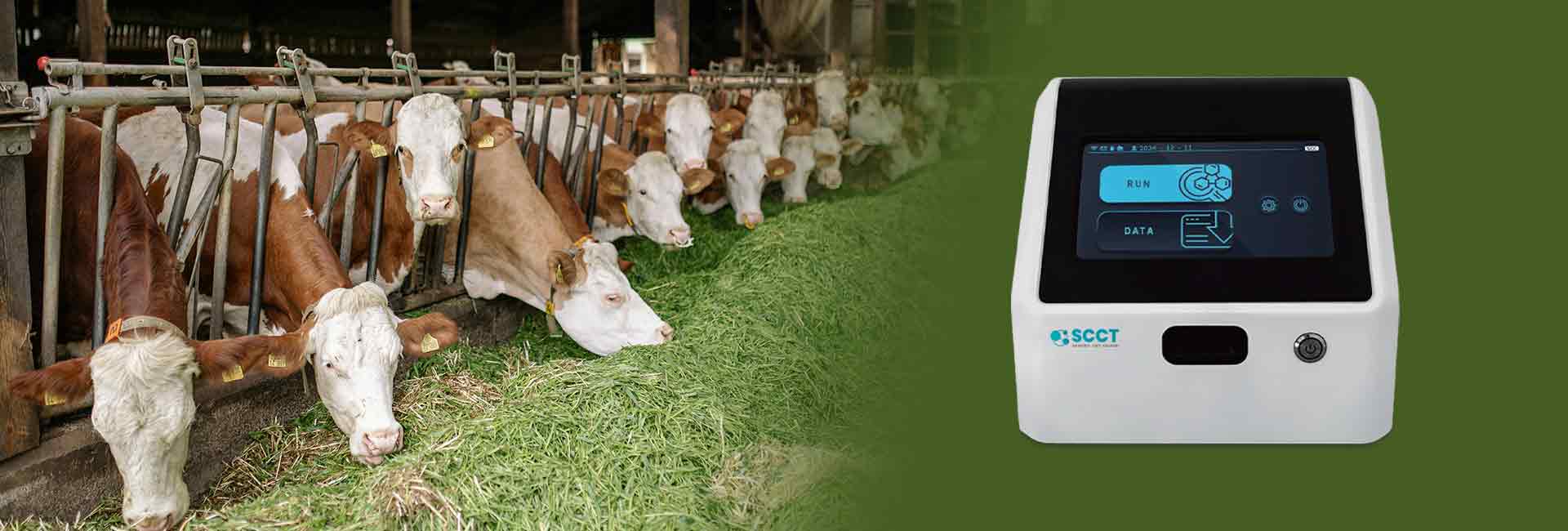

A somatic cell count tester plays a crucial role in monitoring milk quality on dairy farms. When the device does not turn on, users should first check the power source. Staying calm helps in following each troubleshooting step accurately. Quick action prevents inaccurate readings that may hide mastitis cases, which can lead to poor milk quality and financial penalties for dairy producers. Users should always refer to the device’s user manual for model-specific instructions.
Tip: Always keep the user manual close for quick reference during troubleshooting.
Key Takeaways
- Always check the power source and connections first. A loose plug or faulty outlet can prevent the tester from turning on.
- Inspect and replace the battery regularly. A weak or corroded battery can disrupt operations and affect milk quality.
- Look for physical damage on the device. Cracks, moisture, or chemical spills can cause malfunctions.
- Clean contacts and connectors frequently. Dust and oxidation can hinder electrical connections and lead to power issues.
- If troubleshooting fails, contact customer support for assistance. Keeping a record of issues helps diagnose problems faster.
Power Source and Battery
Check Connections and Outlet
A reliable power source is essential for any somatic cell count tester. Users should start by examining all power connections. They need to confirm that the power cord sits firmly in both the device and the wall outlet. Sometimes, a loose plug can prevent the tester from starting. If the device still does not respond, users should try a different outlet. Electrical outlets can fail or lose power, especially in older dairy facilities. Testing another outlet helps rule out this common issue.
Tip: Use a small lamp or phone charger to check if the outlet works before plugging in the somatic cell count tester.
Inspect and Replace Battery
Somatic cell count tester operates with batteries. Users should remove the battery cover and inspect the battery for any signs of corrosion or leakage. A weak or dead battery often causes the device to remain off. They should check the battery’s charge level if the tester has an indicator. If the battery appears old or damaged, replacing it with a new one can solve the problem. Fresh batteries ensure accurate somatic cell counts and help maintain milk quality.
A faulty battery can disrupt daily dairy operations. Regular battery checks prevent unexpected downtime. Keeping spare batteries on hand supports continuous monitoring of bulk tank somatic cell count, which is vital for dairy herd health.
- Checklist for Battery Issues:
- Remove the battery and check for corrosion.
- Test the battery in another device if possible.
- Insert a new battery if the current one seems weak.
- Ensure the battery compartment is clean and dry.
A well-maintained power source and battery system keeps the somatic cell count tester ready for use. This practice supports dairy producers in tracking somatic cell counts and protecting their herds from mastitis.
Device Check for Somatic Cell Count Tester
Look for Damage or Loose Parts
A thorough inspection of the somatic cell count tester helps identify physical issues that may prevent the device from turning on. Users should examine the exterior for cracks, dents, or other signs of mechanical damage. These problems often occur in older equipment or after accidental drops. Moisture can also enter the device, especially in humid dairy environments, leading to corrosion and electrical failure. Chemical spills from cleaning agents or disinfectants may damage internal components and compromise the device’s structure.
The following table summarizes the most common types of damage:
| Type of Damage | Description |
|---|---|
| Mechanical Damage | Physical damage to the machine, especially in older parts, can lead to distortion and malfunction. |
| Moisture Damage | Moisture can cause corrosion and damage to electronic components, affecting the device’s integrity. |
| Chemical Ingress | Chemicals can corrode components and ruin the structure of the device, leading to failure. |
| Electrical Damage | Surges from lightning or power fluctuations can damage the electronics, rendering the device inoperable. |
Cables and connectors deserve special attention. Over time, cables may corrode, fray, or lose insulation. Heavy vibration or rough handling during dairy operations can also cause cable damage. Seals around the device may degrade, allowing moisture to enter and create electrical issues.
Tip: Regular testing and visual checks help prevent unexpected failures and support consistent milk quality.
Reset the Device

Somatic cell count tester includes a reset function. Users should consult the user manual to locate the reset button or follow the recommended reset procedure. A reset can clear minor faults or software glitches that stop the device from starting. If the device remains unresponsive after a reset, further troubleshooting or professional assistance may be necessary.
Routine device checks and resets form an important part of dairy equipment maintenance. These steps ensure accurate somatic cell count readings and help protect the herd from mastitis. Consistent testing supports the overall health of the dairy operation and maintains high standards for milk production.
Troubleshooting and Error Indicators
Review Manual and Error Codes
When a somatic cell count tester fails to power on, users should check the device’s display for any error codes or unusual behavior. Many testers show specific codes that help identify the problem. The user manual often lists these codes and their meanings. For example, a code like I-001 usually signals a low battery. In this case, users should attach the external power supply or place the device in its docking station. Sometimes, the tester may not show any message but acts strangely. Waiting ten seconds and trying to power on again can help. If the device remains unresponsive, users should check the battery pack or connect the power adapter. Persistent issues may require contacting the manufacturer’s support team.
The following table summarizes common error codes related to power issues:
| Error Code | Description | Suggested Action |
|---|---|---|
| I-001 | Battery Low | Attach the external power supply or place the meter in its docking station. |
| — | No Message/Unusual Behavior | Wait 10 s and retry power-on. Check battery pack or connect power adapter. If still unresponsive, contact Roche. |
| — | Automatic Shutdown | Press the power button to reactivate. Default timeout = 5 min (configurable). |
Understanding these codes helps dairy workers quickly restore the tester and maintain milk quality.
Clean Contacts and Connectors
Dirty or oxidized contacts can prevent a somatic cell count tester from turning on. Dust, dirt, and oxidation often build up on connectors, especially in busy dairy environments. Cleaning these areas ensures reliable electrical connections. Specialized contact cleaners work well to remove contaminants. Users should power off the device before cleaning and use a soft cloth or brush for best results. Regular cleaning supports accurate somatic cell count readings and helps protect the quality of milk. This simple maintenance step keeps dairy operations running smoothly.
Note: Cleaning contacts and connectors can resolve many power issues and extend the life of testing equipment.
When to Seek Help or Replacement?
Contact Support for Somatic Cell Counts Issues
If a somatic cell count tester does not turn on after basic troubleshooting, users should contact customer support. Many manufacturers offer technical assistance by phone or email. Support teams can guide users through advanced steps or identify if the device needs professional attention. They may ask for details about the tester, such as the model number, error codes, or recent symptoms. This information helps them provide accurate advice. Quick communication with support can prevent delays in spotting mastitis in dairy cows. Early detection of mastitis supports prevention and reduces the risk of udder infections.
Note: Keeping a record of all troubleshooting steps helps support teams diagnose the problem faster.
Consider Repair or Replacement for Milk Quality
Persistent problems with a somatic cell count tester can threaten milk quality and herd health. If the device remains unresponsive, users should consider repair or replacement. Professional repair services can restore function, but sometimes replacement offers a better long-term solution. Reliable equipment helps dairy workers monitor somatic cell count and improve milk quality. High somatic cell counts often signal mastitis, which can spread quickly among dairy cows. Early action protects the udder from further damage and limits the impact of mastitis-causing pathogen exposure.
A comparison table can help users decide between repair and replacement:
| Situation | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Device under warranty | Contact manufacturer |
| Outdated or damaged device | Replace with new model |
| Minor issue, repair possible | Seek professional repair |
| Frequent breakdowns | Replace for reliability |
Regular maintenance and prompt action support mastitis prevention and treatment. Healthy dairy cows produce better milk, and consistent monitoring helps with early spotting mastitis cases. Protecting the udder and maintaining low somatic cell counts remain key steps in mastitis prevention for every dairy operation.
Conclusion

A somatic cell count tester helps every dairy operation protect milk quality. They should check power sources, inspect for damage, and clean connectors. Quick troubleshooting reduces mastitis risk and keeps dairy cows healthy. If the device still fails, they should contact support or consider replacement. Regular maintenance prevents future problems and supports accurate somatic cell count readings.
FAQ
Why Does My Somatic Cell Count Tester Turn Off Suddenly?
A tester may shut down automatically to save battery life. Some models have a default timeout setting. Users can check the user manual for details. Regular charging helps prevent unexpected shutdowns.
How Often Should Users Clean the Tester’s Contacts?
Users should clean contacts every week. Dust and moisture can build up quickly in dairy environments. Clean contacts help maintain accurate somatic cell count readings and support udder health.
What Should Users Do If the Display Stays Blank?
Users should check the power source first. If the display remains blank, they can try a reset. If the problem continues, contacting customer support is the best option.
Can a Faulty Battery Affect Somatic Cell Count Results?
Yes. A weak or damaged battery can cause errors or incomplete tests. Users should replace old batteries to ensure reliable somatic cell count measurements.
Is Professional Servicing Necessary for All Issues?
Not always. Users can solve many problems by checking connections, cleaning contacts, or replacing batteries. For persistent issues, professional servicing ensures the tester works correctly.